“Methods
We systematically reviewed studies to estimate the risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection among those previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. For this systematic review, we searched scientific publications on PubMed and, the pre-print server, MedRxiv through August 18, 2021... To identify relevant studies with appropriate control groups, we developed the following criteria for studies to be included in the systematic analysis: (1) baseline polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing, (2) a negative comparison group, (3) longitudinal follow-up, (4) a cohort of human participants, i.e., not a case report or case series, and (5) outcome determined by PCR...
Results
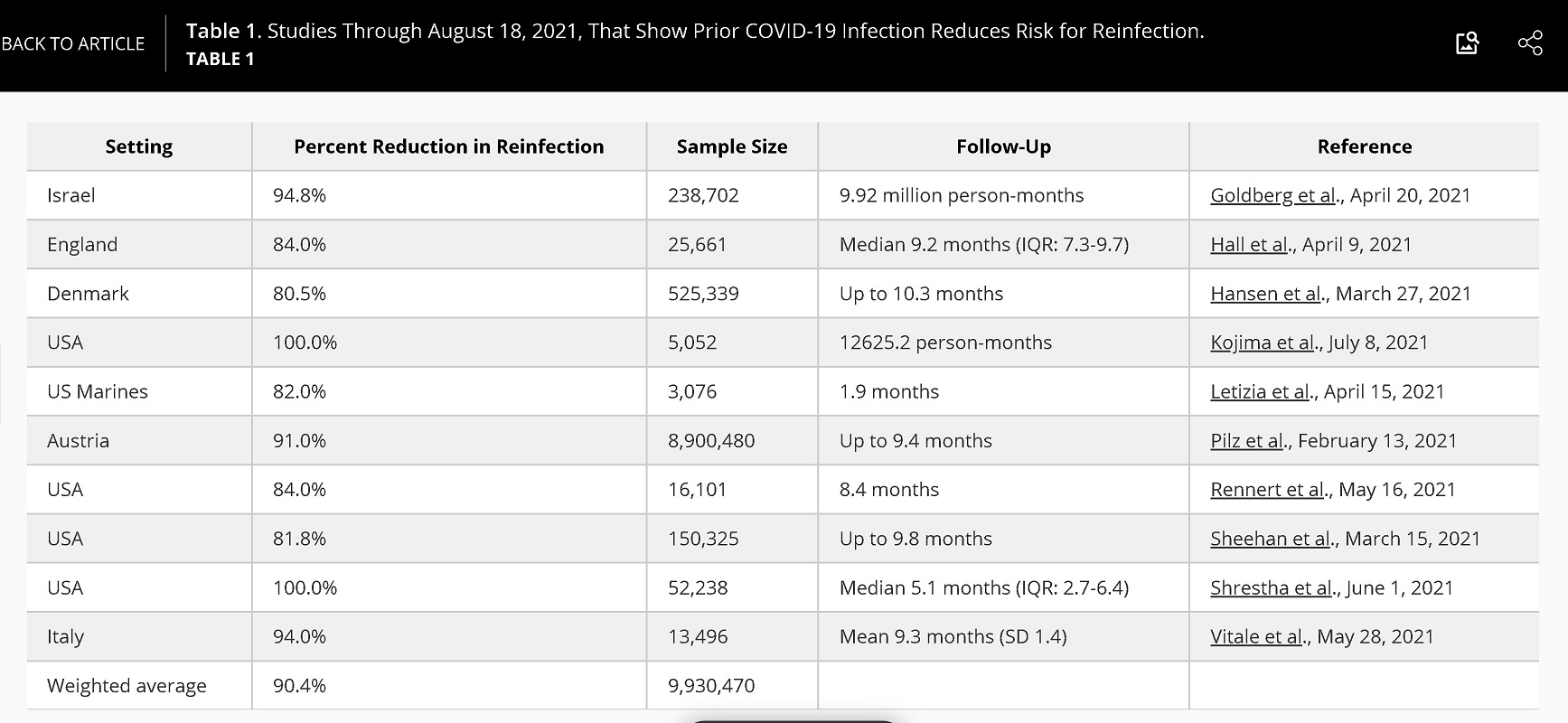
We identified 1,392 reports. Of those reports, 10 studies met the study inclusion criteria from 6 different countries. The total population in the 10 studies included 9,930,470 individuals with a median observation period that ranged from one to 10.3 months.
We found that the relative decreased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection ranged between 80.5 to 100% compared to those without prior infection (See table 1 below). The weighted average risk reduction against reinfection was 90.4%, with a standard deviation of 7.7%. The p-value for percentage reduction was less than 0.01.”
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits non-commercial use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed as specified on the SAGE and Open Access pages (https://us.sagepub.com/en-us/nam/open-access-at-sage
