"Background
.. Mask recommendations and mandates were among the most widely implemented yet highly debated measures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Research on the effectiveness of masking and mask mandates has yielded mixed conclusions. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), widely regarded as the gold standard for evaluating drugs or therapies, have found little to no effect of masking on viral transmission... Excess mortality has gained attention as a proxy for pandemic impact, with studies highlighting its advantages over reported COVID-19 deaths. Nevertheless, no study on mask effectiveness has yet used excess mortality as an endpoint.
A previous analysis of European countries during the 2020–2021 winter suggested that mask usage did not correlate with COVID-19 cases but showed a weak positive correlation with COVID-19 deaths. To further investigate this finding, the present study expands the analysis to a two-year period (2020–2021) and incorporates multiple excess mortality estimation approaches, focusing on 24 European countries for which reliable excess death data are available...
Results
The inclusion criteria for this study was any European country with a population larger than one million and for whom reliable excess death data was available...
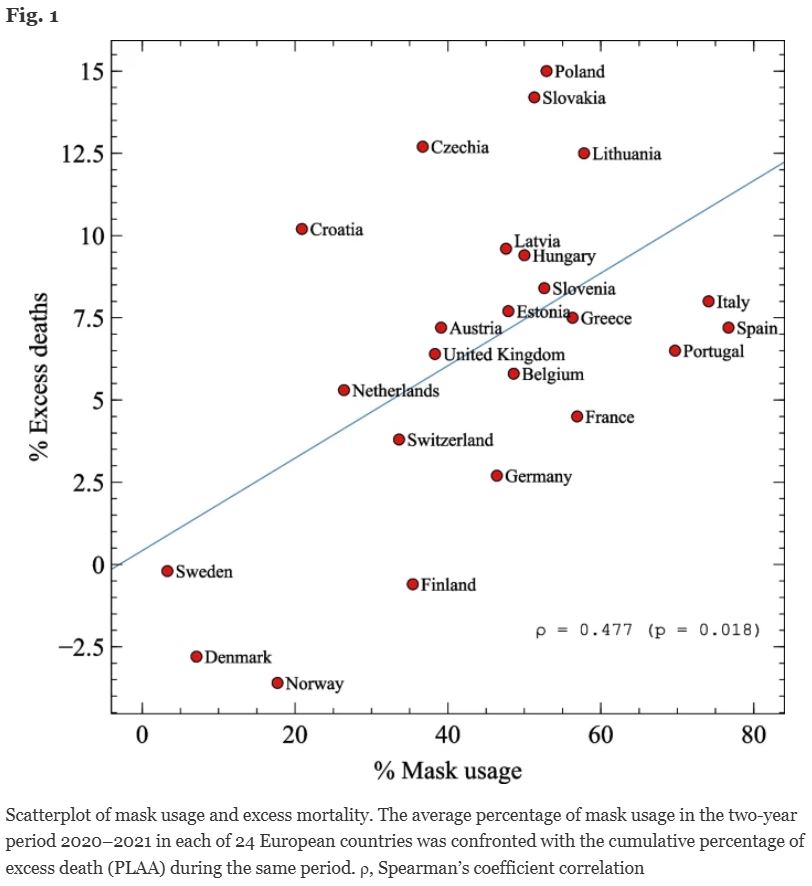
Bivariate correlations: ... It has been previously shown that the average rate of mask usage in Europe during the 6-month period encompassing the winter of 2020–2021 was not associated with the rate of COVID-19 cases, but was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality. Our current analysis, spanning a two-year period, indicates that mask usage exhibited no significant association with COVID-19 case rates (ρ = −0.011). This finding suggests that, when examined at a population level, the widespread use of masks did not appear to have a substantial impact on the transmission of COVID-19 (Table 2). Conversely, the rate of mask usage in Europe showed a moderate positive correlation with PLAA [Per Levitt age adjusted] (ρ = 0.477) (Fig. 1) as well as with all other excess death metrics (PLNAA, eLife, Economist, Lancet, WHO and Multiverse) (Table 2). Mask usage also showed a significant correlation with COVID-19 mortality (ρ = 0.415)...
Discussion
... The main conclusions of this study are twofold: at the population level (1) masks did not reduce COVID-19 transmission, and (2) mask usage is significantly associated with excess mortality."
© The Author(s) 2025
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
