Review Article
Contents include:
2 Main Platforms of Covid-19 Vaccines
2.1 Nucleic acid vaccines
2.2 Viral vector vaccines
2.3 Inactivated virus vaccines
2.4 Protein subunit vaccines
3 Covid Vaccines and Main Serious Adverse Events
3.1 Immunological adverse events
3.1.1 Anaphylaxis
3.2 Cardiac adverse events
3.2.1 Myocarditis and/or pericarditis
3.3 Hematologic adverse events
3.3.1 Vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia
3.4 Neurological adverse events
3.4.1 Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
3.4.2 Guillain–Barré syndrome
3.4.3 Transverse myelitis
3.4.4 Other neurological serious adverse events
"1 Introduction
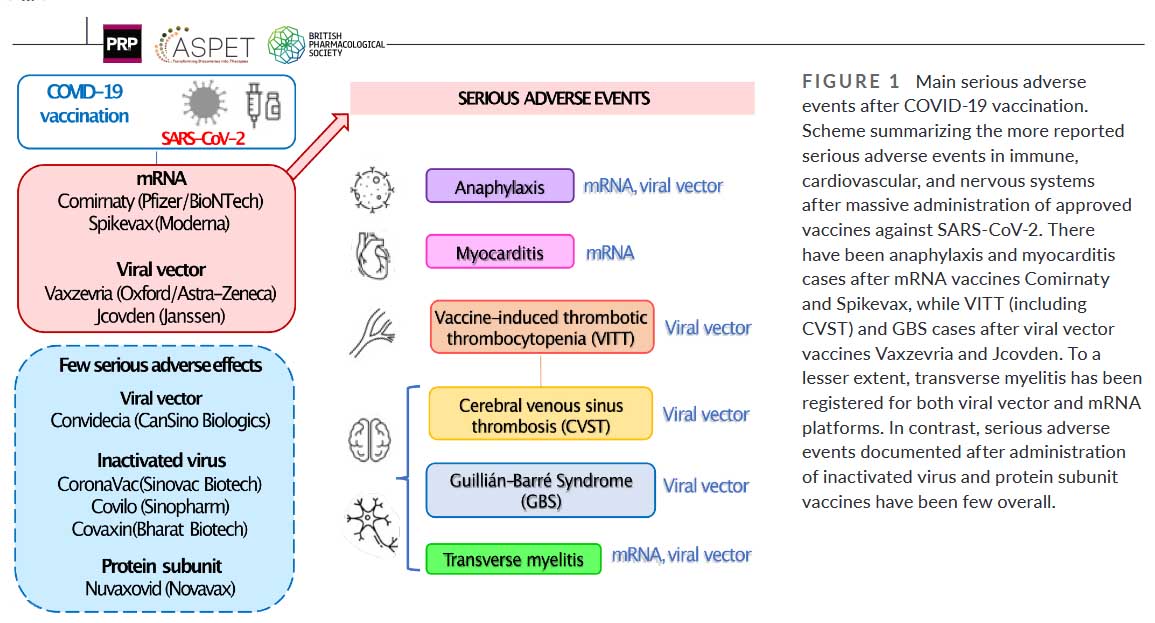
... Among the more reported serious adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination are anaphylaxis, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), myocarditis, Guillain–Barré Syndrome (GBS), and acute transverse myelitis (TM). Given its very low incidence, they were almost not observed during phase 3 clinical trials; their occurrence became evident after the massive worldwide vaccination programs. Hence, there are increasing numbers of case reports, retrospective cohort studies, systematic reviews, meta-analysis, and other studies, aimed to described [sic] them...
Discussion
... Many factors are involved when severe adverse events are presented after vaccination, in which the vaccine (e.g., platform, antigen, formulation) and host characteristics (e.g., genetic background, sex, age, comorbidities, and environment), interact to promote the manifestation of a particular event, especially those of autoimmune origin.
Given that all COVID-19 vaccines with a wide application around the world are based on Spike protein, one could think that differences in number of cases relate to the rest of the components in their formulation. However, it is difficult to establish strict and true comparations between data from different populations and vaccine platforms, and obviously it is important to consider that a higher number of doses have been administered for some of them. So far, the potential association between Ad vector vaccines and VITT seems to be the most sustained by large epidemiological data...
Compared with COVID-19 vaccines based on Ad vector (Oxford/AstraZeneca and Janssen) and mRNA (Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna) vaccines, serious adverse events incidence following inactivated (Sinovac, Sinopharm and Bharat) and protein subunit (Novavax) vaccines have been much lower so far (Figure 1). Therefore, although mRNA and vector vaccines offer advantages and higher efficacy, they might still need further improvements."
© 2024 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
