"Abstract
Myocarditis, typically manifesting as myopericarditis, is among the serious cardiac consequences observed over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. We performed a comprehensive, evidence-based literature synthesis of findings from clinical trial data reanalyses, post-marketing surveillance, large observational studies, and other diverse research sources that help shed light on the phenomenon of myocarditis post SARS-CoV-2 infection versus COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis. Our conclusions refute several claims previously made by public health agencies and professional associations, namely the following: (1) the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Omicron infections have caused more cases of myocarditis than the COVID-19 mRNA immunizations; (2) mRNA vaccine-induced myocarditis is typically mild, transient, and rare, with no long-term sequelae; and (3) the risk-benefit calculus favors continued use of these products despite evidence of more iatrogenic cases. We address each of these misconceptions by applying a combination of epidemiological, clinical, and immunological perspectives...
Introduction
... Temporal evidence from multiple large observational studies and vaccine safety monitoring systems worldwide suggests a causal relationship between the COVID-19 mRNA vaccinations and new-onset myocarditis...
COVID-19 mRNA products are, by definition, gene therapy products that rely on synthetic, modified mRNA (or adenoviral vector DNA), encapsulated within a protective lipid nanoparticle vehicle. These nucleic acids are designed to instruct the ribosomes in the body’s cells to produce the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, the intended target antigen...
Discussion
This narrative review has presented diverse evidence and perspectives highlighting the relatively large contribution of COVID-19 mRNA vaccinations to elevated myocarditis rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Various sources of epidemiological and clinical data collectively highlight an emerging pattern suggesting that the risks of myopericarditis (either specifically defined myocarditis or pericarditis or most often both conditions) associated with COVID-19 vaccination were significantly underreported and/or underestimated by regulatory agencies due to the lack of large-scale prospective cohort studies with baseline and post vaccination assessments (history, ECG, laboratories, cardiac imaging).
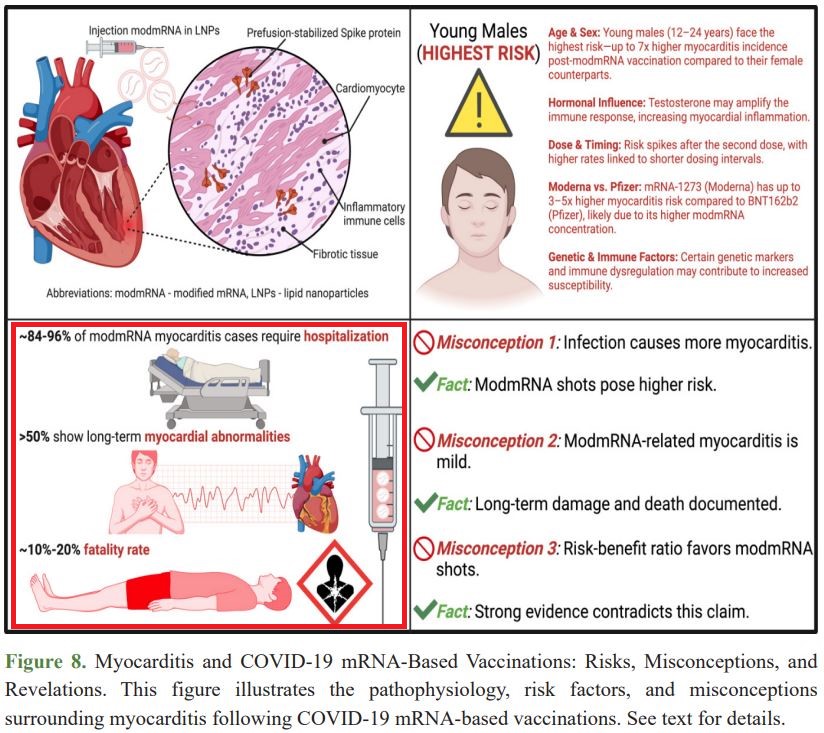
Figure 8 [below] depicts the pathophysiology, risk factors, and misconceptions surrounding myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA-based vaccinations...
Conclusions
... Despite consistent safety signals showing a relatively high risk of myocarditis and its sequelae in younger age groups, public health authorities have defended the continued use of these [vaccine] products...
Given the substantial evidence presented here concerning cardiotoxicity and serious cardiac events in younger generations, we strongly recommend the immediate withdrawal of COVID-19 mRNA products from the market."
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Reseapro Journals.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
