"Abstract
Unheralded cardiac arrest among previously healthy young people without antecedent illness, months or years after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination, highlights the urgent need for risk stratification. The most likely underlying pathophysiology is subclinical myopericarditis and reentrant ventricular tachycardia or spontaneous ventricular fibrillation that is commonly precipitated after a surge in catecholamines during exercise or the waking hours of terminal sleep. Small patches of inflammation and/or edema can be missed on cardiac imaging and autopsy, and the heart can appear grossly normal. This paper reviews evidence linking COVID-19 vaccines to cardiac arrest where unfortunately the majority of victims have had no antecedent clinical evaluation. We propose a comprehensive strategy for evaluating cardiovascular risk post-vaccination, incorporating detailed patient history, antibody testing, and cardiac diagnostics in the best attempt to detect abnormalities before sudden cardiac death...
Introduction
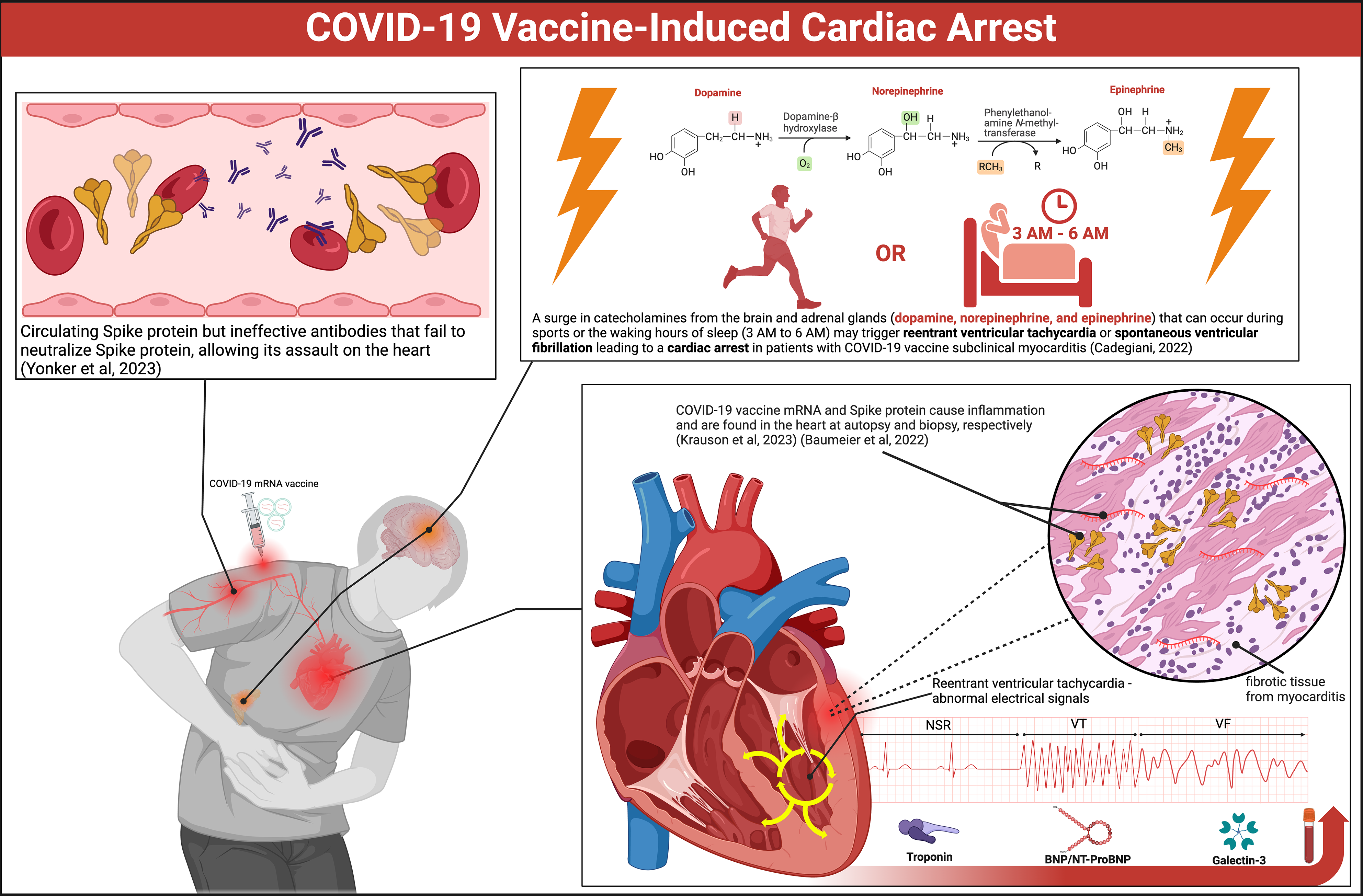
We continue to observe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccinated persons suffer cardiac arrests since the inception of the mass vaccination campaign in late 2020. Figure 1 [First image, below] illustrates the likely mechanisms. Both Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) and Moderna (mRNA-1273) mRNA have been found in human heart muscle at autopsy. Spike protein has been stained in endomyocardial biopsy samples of young men suffering from COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis. Victims have been found to have circulating Spike protein but ineffective antibodies, likely IgG4 subclass, that fail to neutralize Spike protein and allow its assault on the heart...
Rationale for Risk Stratification
Elevated numbers of sudden deaths among athletes after COVID-19 vaccination have raised concerns. Alessandria et al amplified these concerns, demonstrating higher all-cause death risks in COVID-19 vaccinated individuals compared to the unvaccinated. Participants that received 2 doses lost 37% of life expectancy compared to the unvaccinated population during follow-up. The largest COVID-19 vaccine safety study to date with approximately 99 million vaccinated individuals found that the risk of myocarditis was significantly elevated after mRNA COVID-19 vaccinations, with the risk being 510% higher following the second dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine and 186% higher following the second dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine, compared to baseline rates...
Cardiac abnormalities have been observed for at least a year following the initial diagnosis of COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis, suggesting the potential for long-term effect...
Risk Stratification Approach
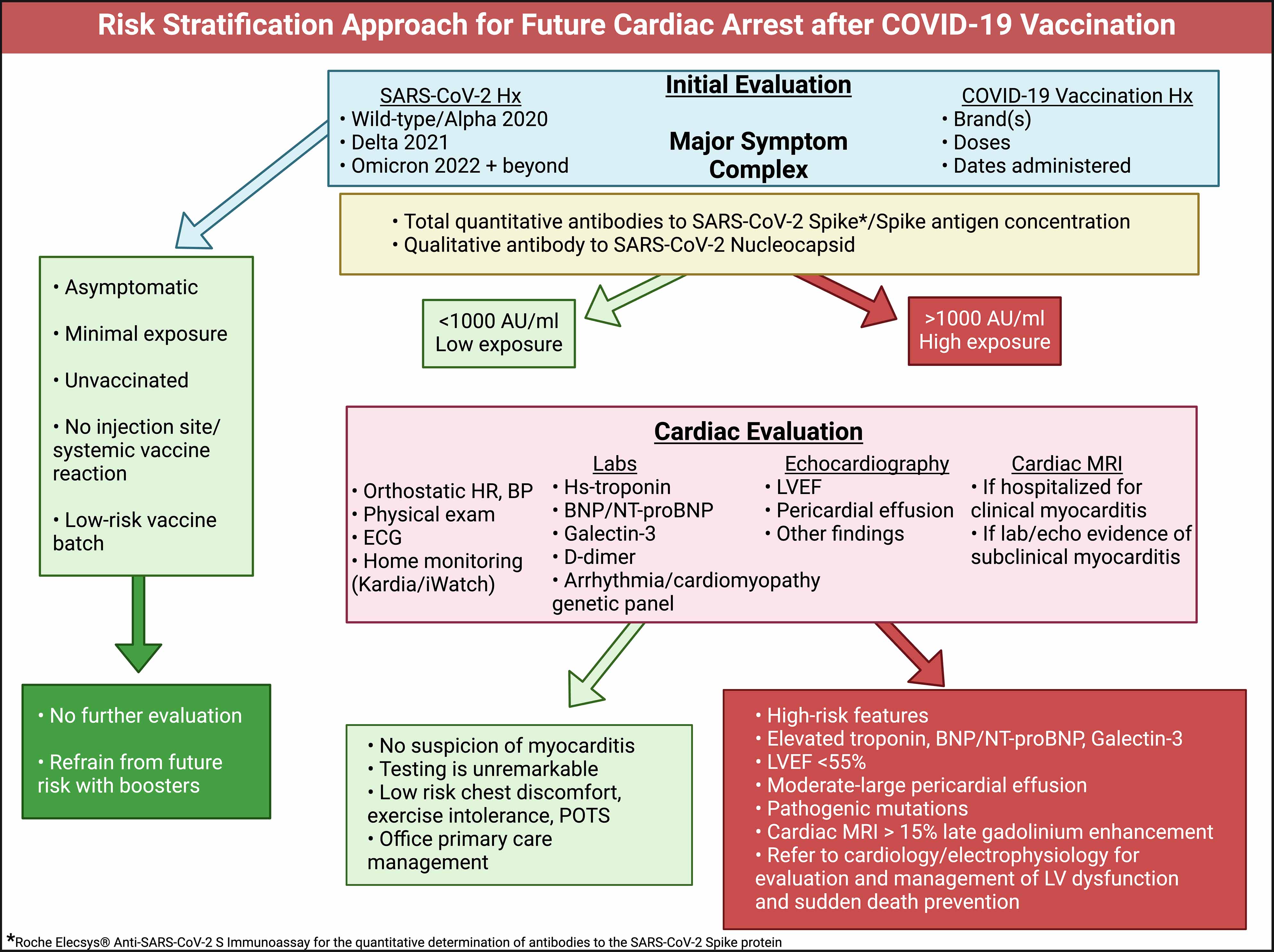
When patients are seen in clinical practice for the initial evaluation of cardiovascular symptoms following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection or vaccination, a proposed approach is outlined in Figure 2 [Second image, below]."
©The Author(s) 2025
This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
On December 13, 2024, Dr. McCullough granted The Covid Index permission to publish Index Entries for his work.
